Effects,of,4,Types,of,Remediation,Agents,on,Reducing,Cd,Contents,in,Soil,and,Rice,on,Cd-contaminated,Farmland
时间:2023-11-05 15:55:02 来源:小苹果范文网 本文已影响 人 
HU Qing-yun, TANG You-gen, ZHANG Zhi-qiang, LUO Ying, ZHANG Xiao-yi, XIAO Huan,AO He-jun*
1. Hengnan County Agricultural and Rural Bureau, Hengyang 421131, PRC;
2. College of Agronomy, Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha 410128, PRC
Abstract A field experiment was carried out in Cd-contaminated rice fields in a county of Hengyang to explore the effects of different types of remediation agents on the contents of soil available Cd and rice Cd, and rice yield by using one rice variety Longliangyouhuazhan, and 4 kinds of remediation agents: DG foliar control agent, SMA microbial inoculant, XFJ organic fertilizer and LXM calcium-and silicon-based passivator as test materials. The results showed that compared with CK, after applying DG foliar control agent, soil available Cd content increased rather than decreased, whereas rice Cd content decreased, not reaching a significant level.When applied with SMA microbial inoculant, soil pH value, soil available Cd and rice Cd contents showed a downward then upward trend with the increase of its application rates. Between 3 levels of SMA treatments, the content of soil available Cd in SMA2 was the lowest, decreased by 8.59% in comparison with CK, contrarily,two other SMA treatments were increasing instead of decreasing in the content of soil available Cd. The application of XFJ organic fertilizer and LXM calcium-and silicon-based passivator increased soil pH value, and reduced soil available Cd and rice Cd contents; the contents of soil available Cd and rice Cd decreased with their application rates increasing. Compared with CK, XFJ3 reduced soil available Cd content by 9.40%, and significantly reduced rice Cd content by 57.28%. In LXM3 treatment, soil available Cd content reduced by 14.57%, rice Cd content was 71.57%lower than CK, reaching the lowest level. In general, LXM calcium-and silicon-based passivator had the best Cd reduction effect, with the optimal application amount of 6 000 kg/hm2.
Key words Rice; Remediation of Cd-contaminated farmland; Foliar control agent;Organic fertilizer; Microbial inoculant; Calcium-and silicon-based passivator; Cd reduction effect
Approximately two-thirds of Chinese population eat rice as their staple foods. As the largest grain crop in China, rice plays an important role in ensuring the food security. According to the sampling results of rice safety in recent years, the Cd content in rice in China exceeded 28.4% of the national standard. Studies have shown that Cd in soil not only has a toxic effect on rice, but also enters human and animal bodies through the food chain and long term consumption of rice with excessive Cd will endanger human health. As the national advanced city of grain production and a national commodity grain base,Hengyang plays an important role in ensuring national food security and promoting the development of agricultural modernization. Due to the development of industrial and agricultural production and population growth along the Xiangjiang River, especially the high polluting enterprises such as mining and beneficiation, smelting and chemical industry are mostly distributed on both banks of the Xiangjiang River, and the emission of heavy metal pollutants continues to accumulate, resulting in the increasingly serious eutrophication of the Xiangjiang River. The Xiangjiang River is the main irrigation water source of Hengyang, and many heavy metals are deposited into the soil through irrigation. Nowadays, the pollution source has been cut off, while the heavy metal in soil still exists. Therefore, in order to ensure food security,it is urgent to control Cd pollution in farmland.
Considering the fact that the Cd pollution in fields was long-lasting and accumulative, and the accumulation of Cd in rice was affected by many factors such as Cd form, variety and temperature,the measures should be adjusted to the actual local situation of pollution. As to the situation of heavy metal pollution in Hengyang, 4 different types of remediation agents were selected for experiments to explore the effects of different remediation agents and their dosage on soil Cd activity and Cd in rice, so as to screen out suitable remediation materials for local areas and provide technical support for protecting the safety of Cd contaminated farmland grain production.
2.1. Test site and materials
The experiement was conducted in 2016 in Denjia Group, Huangtang Village, Songjiang Town,Hengnan County, Hengyang City, Hunan Province.The soil pH value was 6.8~7.7, and the total Cd content was 3.10 mg/kg. According to the soil environmental quality standard GB15618—1995, the soil belonged to the soil with heavy Cd pollution.
The tested rice variety was indica two-line hybrid rice Longliangyouhuazhan. 4 different types of remediation agents were selected in the test: DG foliar control agent (liquid silicon fertilizer), SMA microbial inoculant (Brevibacillus laterosporus
,Bacillus licheniformis
, bioactive calcium and organic carrier),XFJ organic fertilizer (fermented and decomposed organic materials, highly active functional bacteria,feed grade zeolite powder, starch) and LXM calciumand silicon-based passivator (available silicon≥15%;available calcium≥40%).2.2. Experiemental design
The experiment was designed with randomized block, as shown in Table 1, 11 treatments with three replications, a total of 33 plots, and the area of each plot was 20 m. The plots were separated by ridges and covered with agricultural film, single row and single irrigation, field management and fertilization should be carried out according to local conventional methods. Except that DG foliar control agent was sprayed at the early booting stage and early filling stage of rice, other remediation agents were applied with base fertilizer before ploughing, and transplanting after ploughing for 4~7 d.
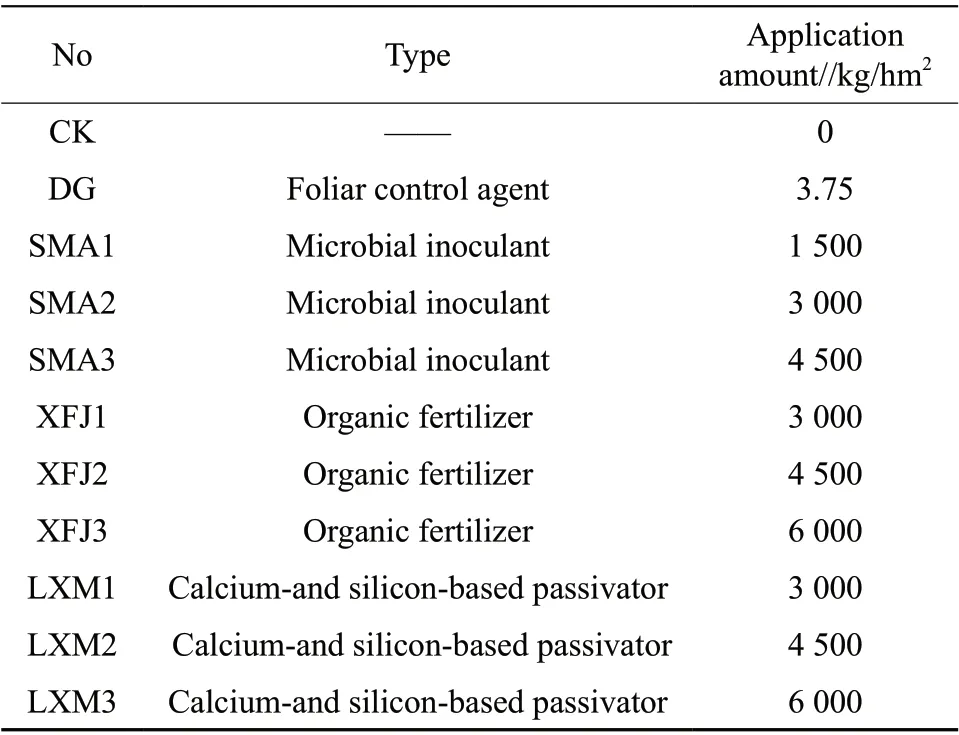
Table 1 Types of remediation agents and their application amount
2.3. Sample collection and determination
At the mature stage, 5-point sampling method was used to collect soil samples and plant samples of 0~20 cm tillage layer. After the soil samples were taken back, dried naturally and ground, and sundries such as gravel and plant residues shall be removed,passed through 10 mesh and 100 mesh nylon screens for standby. After plant samples were sampled, then threshed and bagged, fixated in the oven at 105 °C for 30 min, and then dried at 80 °C to constant weight,then the grains were beaten into brown rice, crushed with a stainless steel mill, passed through 100 mesh nylon screen and for standby.
The soil pH value was determined by site method (water-to-soil ratio was 2.5 ∶1); the available Cd in soil was extracted by DTPA reagent, filtration was performed after oscillation, the Cd concentration in solution was determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, Agilent 7700x,USA); Cd in brown rice was digested by microwave and the Cd concentration in solution was determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry; at the mature stage, each plot was harvested and threshed to measure the yield, and the yield was calculated according to 13.5% of water content.
2.4. Data analysis
Excel 2016 was used for data processing and SPSS 25.0 was used for statistical analysis.
3.1. Effects of different remediation agents on soil pH value
It can be seen from Fig.1, the application of SMA microbial inoculant significantly reduced the soil pH value. Compared with CK, the soil pH value decreased by 0.93~1.07 units, and the decrease range was 12.4%~13.3%. After the application of XFJ organic fertilizer and LXM calcium-and silicon-based passivator, the soil pH value increased by 0.2~0.3 units, with an increase range of 2.7%~4.0%, which was significantly higher than that of the treatment with SMA microbial inoculants. The application of DG foliar control agent was foliar spray, and had no direct effect on soil pH value. Different application doses of the same remediation agent had no significant effects on soil pH value.
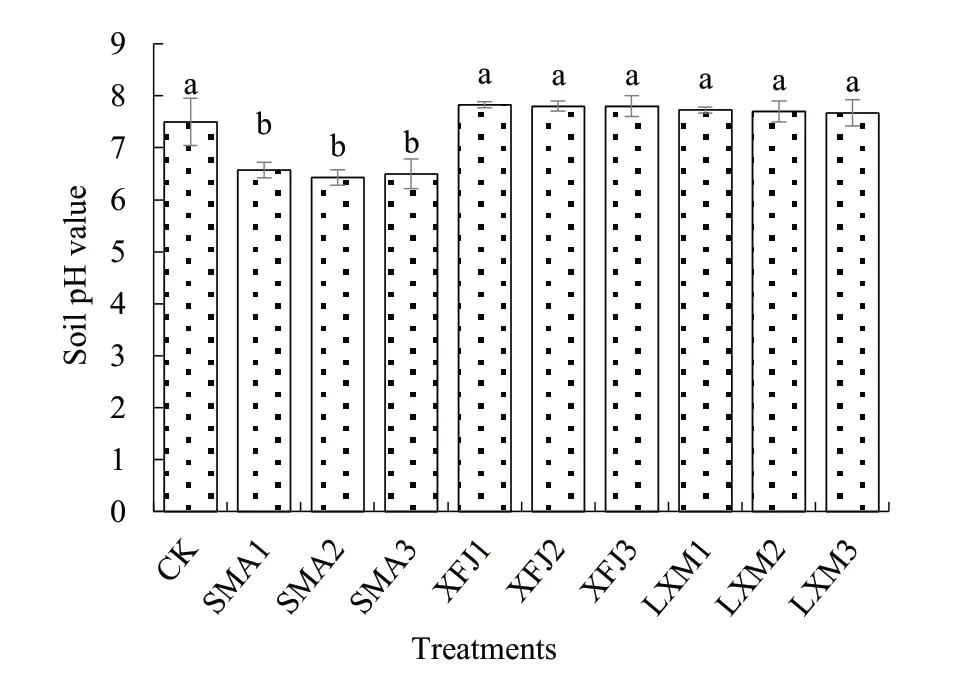
Fig. 1 Effects of different remediation agents on soil pH value
3.2. Effects of different remediation agents on available Cd content in soil
According to Fig. 2, the application of XFJ organic fertilizer and LXM calcium-and silicon-based passivator could reduce the available Cd content in soil; compared with CK, the average decreases were 2.82% and 6.79% respectively. However, after the application of DG foliar control agent and SMA microbial inoculant (except 3 000 kg/hmtreatment),the available Cd content in soil increased instead of decreased, indicating that these two remediation agents activated part of Cd and increased the available Cd content in soil. The effects of different application doses of the same remediation agent on available Cd content in soil showed different trends. Compared with CK, the application of low concentration SMA microbial inoculant, XFJ organic fertilizer and LXM calcium-and silicon-based passivator could increase available Cd content in soil, whereas the amount did not reach a significant level. In SMA treatments, the available Cd content in soil of SMA2 was the lowest, which was 2.353 mg/kg, decreased by 8.59% compared with CK. After applying XFJ organic fertilizer and LXM calcium-and silicon-based passivator, the available Cd content in soil treated with high concentration were the lowest (XFJ3 and LXM3), medium concentration treatment (XFJ2 and LXM2) took the second place; compared with other treatments, the available Cd content in soil treated with XFJ3 and LXM3 was lower, which were 2.332 and 2.199 mg/kg respectively, and decreased by 9.40%and 14.57% compared with CK.
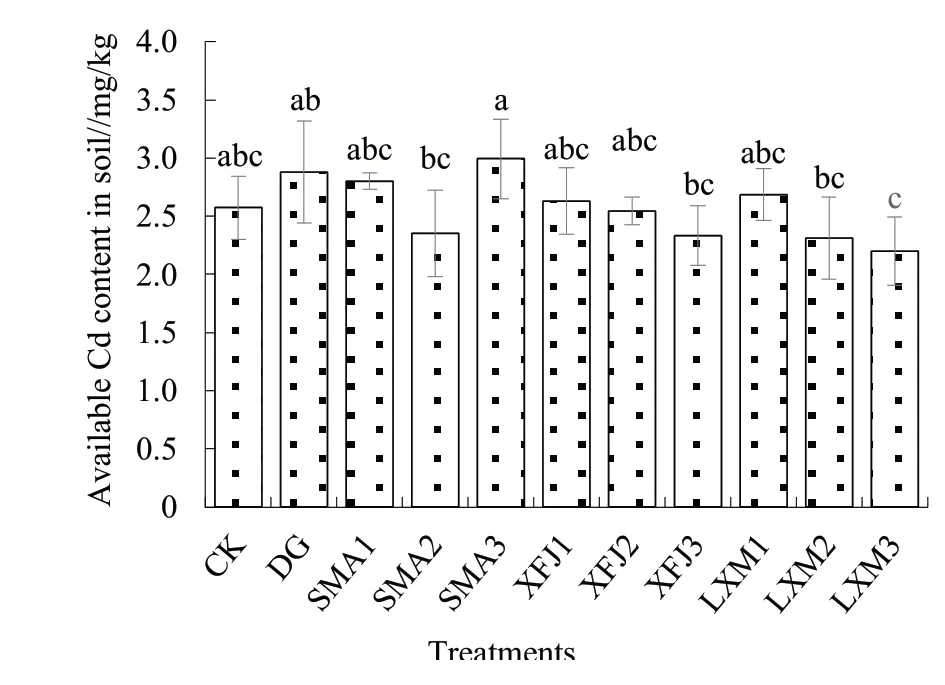
Fig. 2 Effects of different remediation agents on the content of available Cd in soil
3.3. Effects of different remediation on the Cd content in brown rice
As shown in Fig. 3, remediation agents can reduce the Cd content in brown rice, whereas the effects of different remediation agents were different.Compared with CK, DG foliar control agent and SMA microbial inoculant could reduce the Cd content in brown rice, whereas the effect was not significant.Compared with CK, XFJ organic fertilizer and LXM calcium-and silicon-based passivator significantly reduced the Cd content in brown rice, with an average decrease of 50.88% and 69.99% respectively, and there was no significant difference between the two remediation agents. The different application doses of the same remediation agent had no significant effect on the Cd content in brown rice, whereas the Cd content in brown rice decreased gradually with the increase of the application dose of remediation agent. With 3 remediation agents, the Cd contents in brown rice in high concentration (SMA3, XFJ3 and LXM3) was the lowest, followed by medium concentration treatments(SMA2, XFJ2 and LXM2). The Cd content in brown rice treated with XFJ3 and LXM3 was significantly lower than that of CK and DG, which decreased by 57.28% and 71.57% respectively compared with CK.

Fig. 3 Effects of different remediation agents on the Cd content in brown rice
3.4. Effects of different remediation on the yield of rice
As shown in Fig. 4 that except XFJ1 treatment,other treatments could improve rice yield to varying degrees, with an increase range of 0.37%~5.63%.For the yield of different treatments, it was shown a order of SMA2>SMA3>DG>LXM3>XFJ2>LXM2>LXM1>SMA1>XFJ3>CK>XFJ1. The effects of different application doses of the same remediation agent on rice yield were inconsistent. SMA (microbial agent), XFJ (organic fertilizer) and LXM (calcium-and silicon-based passivator) gave the lowest yield in their low concentration, and XFJ1 gave the lowest yield,which was 7.59% lower than CK. The yield of SMA2 treatment was the highest, which was 9 160.95 kg/hm,increased by 5.63% than that of the CK.
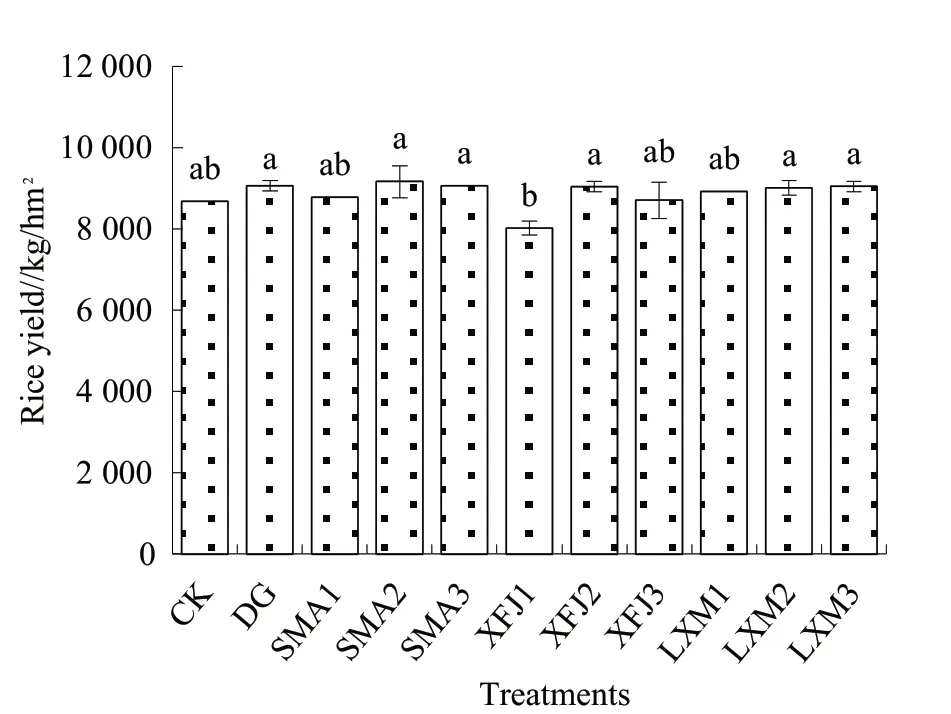
Fig. 4 Effects of different remediation agents on rice yield
Cd uptake by rice was affected by soil pH value,CEC, organic matter and ionic interaction, while soil pH value was one of the main factors affecting of Cd availability. The higher the soil pH value,the weaker the activity of Cd in soil. The results showed that the application of XFJ organic fertilizer and LXM calcium-and silicon-based passivator could increase the soil pH value and reduce the available Cd content in soil. This was because a large amount of ammonium ions would be produced after the application of organic fertilizer so that the soil pH value increased. At the same time, the application of organic fertilizer could increase the organic matter content in soil, the functional groups in organic matter,such as carboxyl and phenolic hydroxyl groups, could effectively adsorb CD in soil and thereby the available Cd content in soil decreased. After adding calciumand silicon-based passivators, because they were rich in alkaline metal compounds such as Ca and Si,they released a large number of hydroxyl ions under hydrolysis, which can improve the soil pH value. Moreover, there was adsorption between Si and Cd, which can form silicon-cadmium polymer, so as to reduce the available Cd content in soil. These two remediation agents can reduce the available Cd content in soil by relying on their own nutrient elements or by increasing soil pH value. The soil pH value decreased significantly after the application of SMA microbial inoculant, because the growth and reproduction of acid producing bacteria led to the accumulation of organic and inorganic acids.Therefore, the available Cd content in SMA1 and SMA3 treatment increased, while the reason why the available Cd content decreased rather than increase in SMA2 treatment needed to be further studied.
There were two ways to reduce the Cd content in brown rice. One was making the bio-availability in soil decrease and another one was preventing rice’s organs from transporting Cd to grains. The main components of 4 remediation agents used in this test contained Ca and Si. There was competition between Ca and Cd, and this competition was not only reflected in the root cell membrane, but also in the transporters in rice, which reduced the absorption of Cd by rice.Si could form silicon-cadmium complex oxide with Cd in plants, inhibited the transport of Cd from rice to aboveground, and reduced the Cd content in brown rice. In this experiment, the application of 4 remediation agents had no significant effect on the available Cd content in soil, whereas significantly reduced the Cd content in brown rice. It may be attributed to that the application of remediation agents inhibited the absorption and transport of Cd in rice,nevertheless, this needs to be confirmed by further research.
LXM calcium-and silicon-based passivator(available silicon≥15%; available calcium≥40%) had the best resistance and control effect on Cd in brown rice, and the Cd content in brown rice decreased with the increase of application amount. The Cd content in brown rice with 6 000 kg/kmLXM calcium-and silicon-based passivator was the smallest, whereas it did not reached the safe edible national standard. On the one hand, the test site was a Cd heavily polluted area. On the other hand, the use of remediation agents to reduce Cd to a certain extent could not be achieved overnight, and it needed to be applied for many years to achieve the ideal effect. The physical and chemical properties of soil were significantly improved by applying the remediation agents, and the contents of soil organic matter and trace elements such as calcium and silicon increased, which was conducive to the normal growth and development of rice.
A suitable remediation agent can not only reduce the Cd content in brown rice, but also have no negative impact on the growth and yield of rice.The results showed that the application of 4 kinds of remediation agents could reduce the Cd content in brown rice, especially the application of 6 000 kg/hmLXM calcium-and silicon-based passivator had the best effect on reducing Cd in brown rice and increasing rice yield.

